

- #Wep vs wpa security wireless cracked
- #Wep vs wpa security wireless upgrade
- #Wep vs wpa security wireless Pc
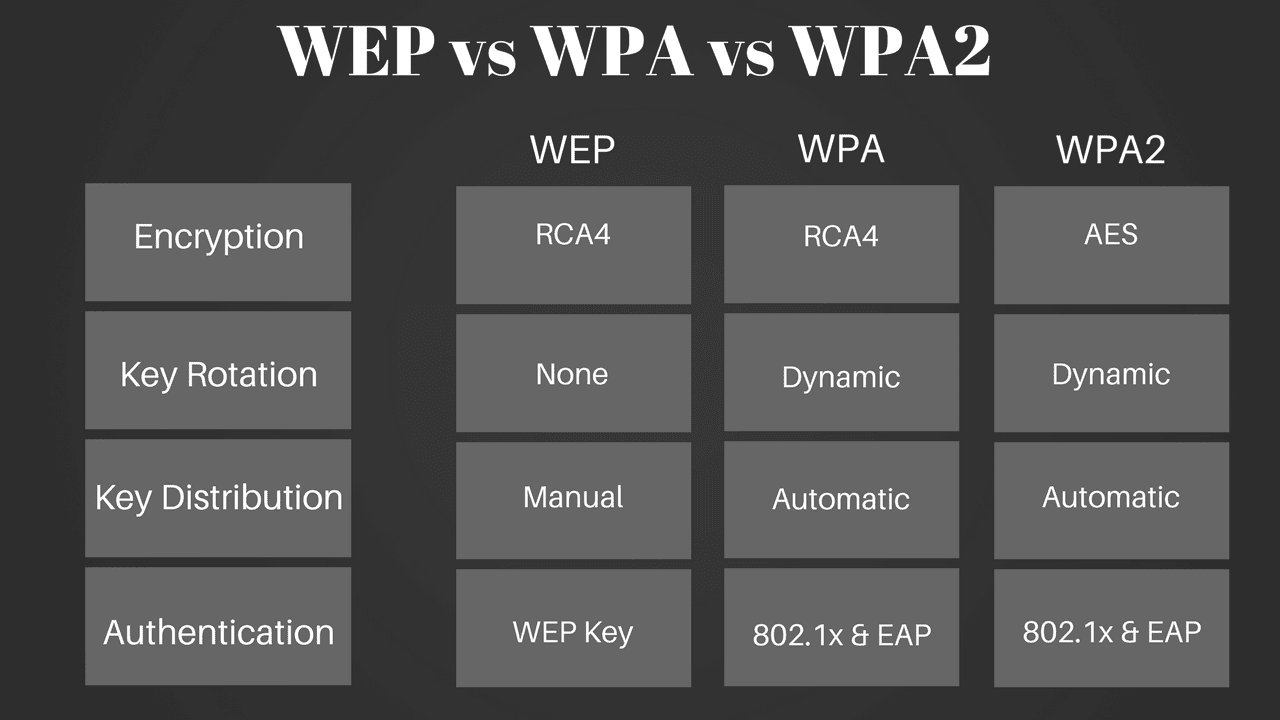
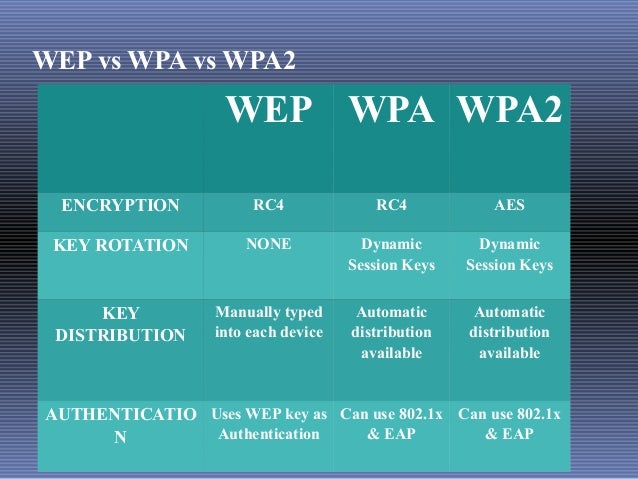
The ability to enter a network while mobile has great benefits. Many laptop computers have wireless cards pre-installed. Enterprises often enforce security using a certificate-based system to authenticate the connecting device, following the standard 802.11X. WPA2 uses an encryption device that encrypts the network with a 256-bit key the longer key length improves security over WEP.
#Wep vs wpa security wireless upgrade
The current standard is WPA2 some hardware cannot support WPA2 without firmware upgrade or replacement. WPA was a quick alternative to improve security over WEP. WEP was superseded in 2003 by WPA, or Wi-Fi Protected Access.
#Wep vs wpa security wireless cracked
It is a notoriously weak security standard: the password it uses can often be cracked in a few minutes with a basic laptop computer and widely available software tools. WEP is an old IEEE 802.11 standard from 1997. The most common type is Wi-Fi security, which includes Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA). The term may also refer to the protection of the wireless network itself from adversaries seeking to damage the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the network. Wireless security is the prevention of unauthorized access or damage to computers or data using wireless networks, which include Wi-Fi networks.
#Wep vs wpa security wireless Pc
WPA2 Enterprise verifies network users through a server.Ĭomputer Networking Free Computer Help Online Computer Tips PC Troubleshooting WEP vs.An example wireless router, that can implement wireless security features WPA2 Personal protects unauthorized network access by utilizing a setup password. It defines new encryption key protocols including the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). 802.11i describes the encrypted transmission of data between systems of 802.11a and 802.11b wireless LANs. WPA2 is based on the IEEE 802.11i standard and provides government grade security. It provides WiFi users with a higher level of assurance that only authorized users can access their wireless networks. WPA2 is the latest implementation of WPA and provides stronger data protection and network access control. WPA is compatible with many older access points and network cards. The TKIP encryption algorithm is stronger than the one used by WEP. This allows key changes to occur on a frame by frame basis and to be automatically synchronized between the access point and the wireless client. The encryption key is changed after every frame using TKIP. WPA is able to achieve over 500 trillion possible key combinations and re-keying of global encryption keys is required. It bridges the gap between WEP and 802.11i (WPA2) networks. WPA uses Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), which is designed to allow WEP to be upgraded through corrective measures that address the existing security problems. WPA is a much improved encryption standard that delivers a level of security beyond anything that WEP can offer. WiFi compliance ensures interoperability between different manufacturer’s wireless equipment. WPA (WiFi Protected Access) is the new security standard adopted by the WiFi Alliance consortium. Most wireless networks that use WEP have one single WEP key shared between every node on the network. This gives hackers plenty of time to monitor and hack into WEP enabled networks. As a result, system administrators and users generally use the same keys for long periods of time. 802.11 doesn’t provide any functions that support the exchange of keys among stations. The static nature of the shared secret keys is its weakness. The passphrase you enter is converted into hex keys.
The WEP concept of using a passphrase is introduced so that you do not have to enter complicated strings for keys manually.

WEP is not difficult to crack, and using it reduces performance slightly. The Access Point and the client must know the codes in order for it to function. WEP has three settings: Off (no security), 64-bit (weak security) and 128-bit (higher security). WEP only encrypts data between 802.11 stations. The receiving station, such as an access point performs decryption upon receiving the frame. The network card encrypts the data before transmission using an RC4 stream cipher provided by RSA Security. WEP is defined in the 802.11b standard and aims to provide security by encrypting data over radio waves so that it is protected as it is transmitted from one end point to another. WEP works by using secret keys, or codes to encrypt data. WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) was originally intended to give you the same or similar level of security as on a wired network but it turns out that it does not.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
